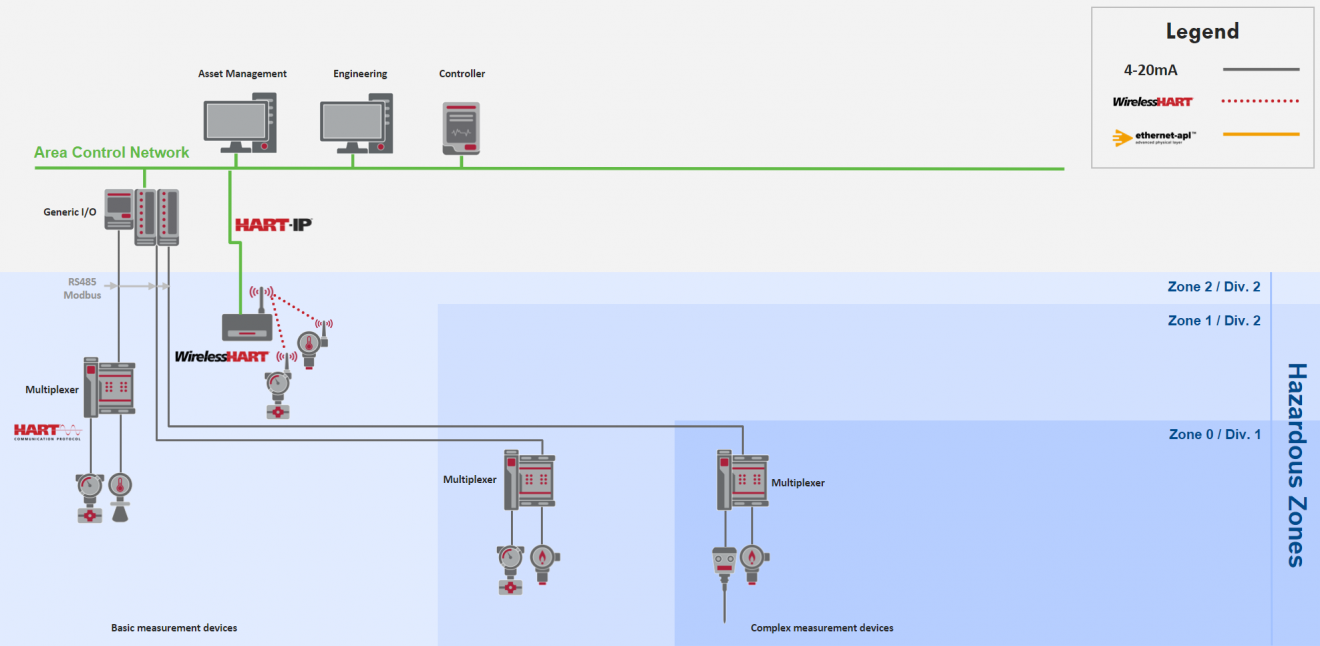
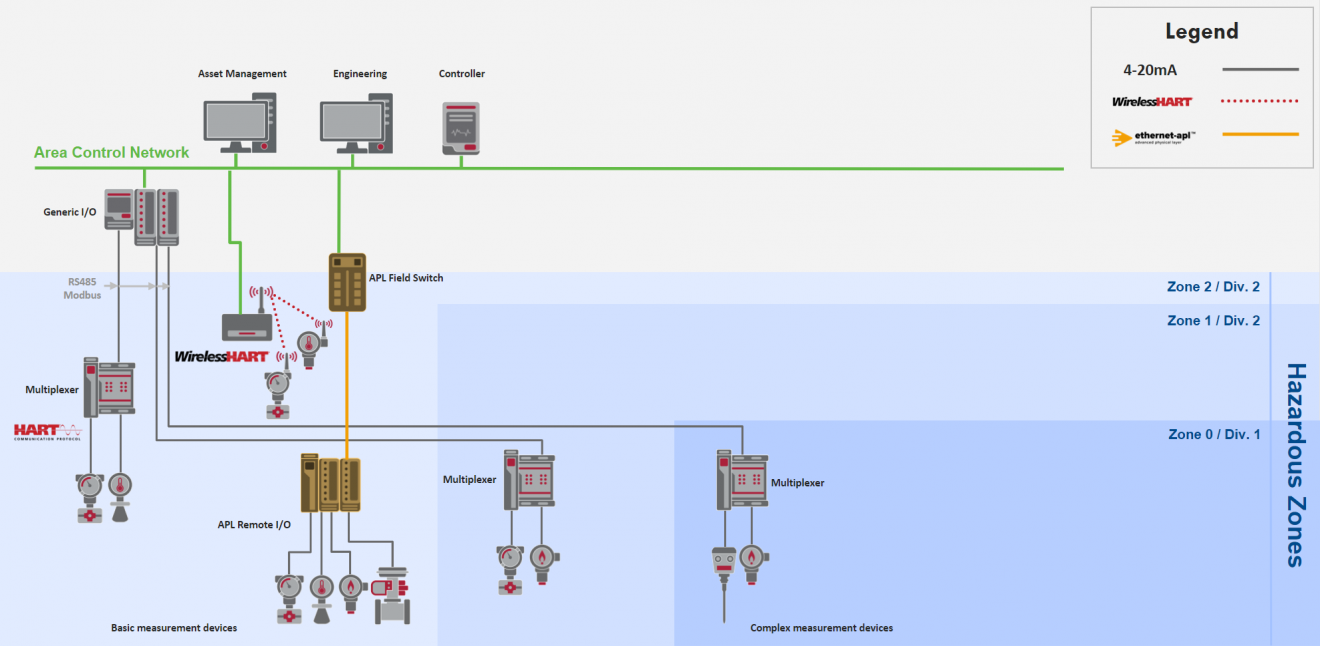
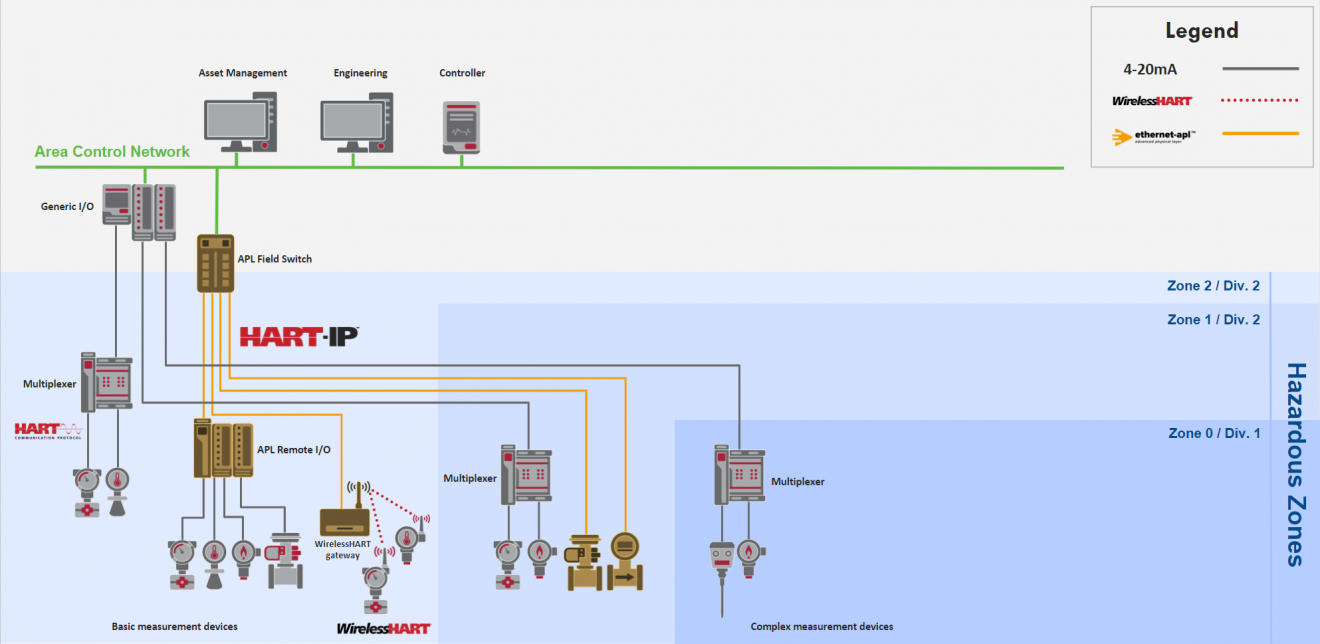
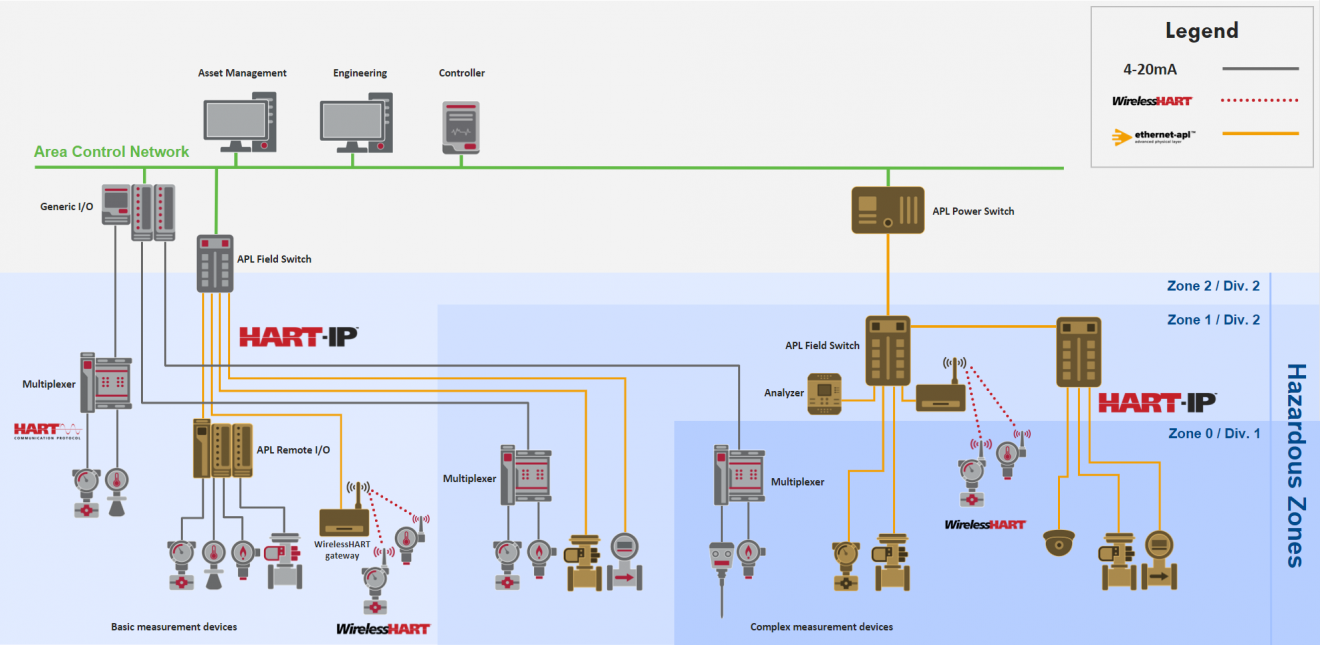
Transitioning to HART-IP
Today, the HART Communications Protocol is used in most of the process automation plants around the world. The technology is well known, reliable and easy to use.
For the process automation world to transform to full digital, a physical layer is required that meets the performance and safety needs of the industry while providing flexible networking design, speed, and security that the IT world has enjoyed for many years.
Ethernet-APL is that physical layer, and when coupled with the IP enabled version of HART - HART-IP - provides the same familiarity, reliability, and ease of use that has made HART the dominant application protocol in process automation.
Watch how your facility can transition to HART-IP and Ethernet-APL.
Watch Paul Sereiko, Director of Marketing at FieldComm Group, explain the process of transition on YouTube.